Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of bones and teeth. It is characterized by the absence or hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the clavicles (collarbones) and delayed ossification (bone formation) of the skull. As a result, people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia may have a distinctive appearance, including a broad forehead, widely spaced eyes, a small chin, and short stature.
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia can also affect the development of teeth. People with this condition may have missing or peg-shaped teeth, and their teeth may be more susceptible to cavities and other dental problems. In some cases, actor cleidocranial dysplasia can also lead to other health problems, such as hearing loss, vision problems, and joint pain.
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is caused by mutations in the RUNX2 gene. This gene is responsible for regulating the development of bones and teeth. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene can lead to the production of a non-functional RUNX2 protein, which in turn disrupts the normal development of bones and teeth.
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is a lifelong condition, but there is no cure. Treatment focuses on managing the symptoms of the condition and improving the quality of life for people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia. Treatment may include surgery to correct bone deformities, dental care to address dental problems, and physical therapy to improve joint function.
Actor Cleidocranial Dysplasia
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of bones and teeth. It is characterized by the absence or hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the clavicles (collarbones) and delayed ossification (bone formation) of the skull. As a result, people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia may have a distinctive appearance, including a broad forehead, widely spaced eyes, a small chin, and short stature.
- Genetic: Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is caused by mutations in the RUNX2 gene, which is responsible for regulating the development of bones and teeth.
- Skeletal: The most common skeletal features of actor cleidocranial dysplasia are the absence or hypoplasia of the clavicles and delayed ossification of the skull.
- Dental: People with actor cleidocranial dysplasia may have missing or peg-shaped teeth, and their teeth may be more susceptible to cavities and other dental problems.
- Growth: Actor cleidocranial dysplasia can lead to short stature and other growth problems.
- Appearance: People with actor cleidocranial dysplasia may have a distinctive appearance, including a broad forehead, widely spaced eyes, a small chin, and short stature.
- Mobility: The absence or hypoplasia of the clavicles can lead to limited mobility in the shoulders and arms.
- Hearing: Actor cleidocranial dysplasia can lead to hearing loss in some cases.
- Vision: Actor cleidocranial dysplasia can lead to vision problems in some cases.
- Joint pain: Actor cleidocranial dysplasia can lead to joint pain in some cases.
- Treatment: There is no cure for actor cleidocranial dysplasia, but treatment can help to manage the symptoms of the condition and improve the quality of life for people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia.
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is a rare condition, but it can have a significant impact on the lives of those who have it. By understanding the key aspects of actor cleidocranial dysplasia, we can better understand the challenges that people with this condition face and how we can support them.
Genetic
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of bones and teeth. It is caused by mutations in the RUNX2 gene, which is responsible for regulating the development of bones and teeth. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene can lead to the production of a non-functional RUNX2 protein, which in turn disrupts the normal development of bones and teeth.
The RUNX2 gene is essential for the formation of bones and teeth. It is responsible for regulating the expression of other genes that are involved in bone and tooth development. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene can lead to a decrease in the production of these other genes, which in turn can lead to the development of actor cleidocranial dysplasia.
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is a lifelong condition, but there is no cure. Treatment focuses on managing the symptoms of the condition and improving the quality of life for people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia. Treatment may include surgery to correct bone deformities, dental care to address dental problems, and physical therapy to improve joint function.
Understanding the genetic basis of actor cleidocranial dysplasia is important for several reasons. First, it can help to identify people who are at risk for developing the condition. Second, it can help to develop new treatments for actor cleidocranial dysplasia. Third, it can help to provide support and information to people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia and their families.
Skeletal
The skeletal features of actor cleidocranial dysplasia are directly related to the underlying genetic cause of the condition. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene lead to the production of a non-functional RUNX2 protein, which in turn disrupts the normal development of bones and teeth. This disruption of normal bone development leads to the absence or hypoplasia of the clavicles and delayed ossification of the skull.
The absence or hypoplasia of the clavicles is a hallmark of actor cleidocranial dysplasia. The clavicles are the bones that connect the sternum to the shoulder blades. In people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia, the clavicles may be completely absent or they may be underdeveloped. This can lead to a number of problems, including shoulder instability, limited range of motion in the arms, and an increased risk of dislocation.
Delayed ossification of the skull is another common skeletal feature of actor cleidocranial dysplasia. Ossification is the process by which bones are formed. In people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia, the ossification of the skull is delayed, which can lead to a number of problems, including an increased risk of head injuries, developmental delays, and intellectual disability.
Understanding the connection between the skeletal features of actor cleidocranial dysplasia and the underlying genetic cause of the condition is important for several reasons. First, it can help to identify people who are at risk for developing the condition. Second, it can help to develop new treatments for actor cleidocranial dysplasia. Third, it can help to provide support and information to people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia and their families.
Dental
The dental features of actor cleidocranial dysplasia are directly related to the underlying genetic cause of the condition. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene lead to the production of a non-functional RUNX2 protein, which in turn disrupts the normal development of bones and teeth. This disruption of normal tooth development leads to the missing or peg-shaped teeth and increased susceptibility to cavities and other dental problems that are characteristic of actor cleidocranial dysplasia.
Missing or peg-shaped teeth are a common feature of actor cleidocranial dysplasia. Peg-shaped teeth are small, cone-shaped teeth that are often widely spaced. Missing or peg-shaped teeth can make it difficult to eat, speak, and smile. People with actor cleidocranial dysplasia may also have other dental problems, such as cavities, gum disease, and malocclusion (bad bite).
The dental problems associated with actor cleidocranial dysplasia can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. Missing or peg-shaped teeth can make it difficult to eat and speak, and they can also lead to social problems. Cavities and gum disease can be painful and can lead to tooth loss. Malocclusion can make it difficult to bite and chew food, and it can also lead to jaw pain and headaches.
Understanding the connection between the dental features of actor cleidocranial dysplasia and the underlying genetic cause of the condition is important for several reasons. First, it can help to identify people who are at risk for developing the condition. Second, it can help to develop new treatments for actor cleidocranial dysplasia. Third, it can help to provide support and information to people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia and their families.
Growth
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of bones and teeth. One of the most common features of CCD is short stature. People with CCD may also have other growth problems, such as delayed puberty, delayed bone age, and small hands and feet.
- Skeletal growth
The skeletal growth problems associated with CCD are caused by mutations in the RUNX2 gene. This gene is responsible for regulating the development of bones and teeth. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene can lead to a decrease in the production of bone-forming cells, which in turn can lead to short stature and other skeletal growth problems.
- Growth hormone deficiency
Some people with CCD also have growth hormone deficiency. Growth hormone is a hormone that is responsible for stimulating growth in children and adolescents. Growth hormone deficiency can lead to short stature, delayed puberty, and other growth problems.
- Other factors
There are a number of other factors that can contribute to the growth problems associated with CCD. These factors include malnutrition, chronic illness, and certain medications.
The growth problems associated with CCD can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life. Short stature can lead to social problems, such as bullying and discrimination. Growth hormone deficiency can also lead to a number of health problems, such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
There is no cure for CCD, but there are a number of treatments that can help to improve growth and development. These treatments include growth hormone therapy, nutritional support, and physical therapy.
Appearance
The distinctive appearance associated with actor cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is primarily caused by the underlying genetic defect that affects bone and tooth development. The RUNX2 gene, which plays a crucial role in bone formation, is mutated in individuals with CCD, leading to disruptions in the normal development of facial and skeletal structures.
- Broad forehead
The broad forehead seen in CCD results from delayed ossification of the skull. Ossification, the process of bone formation, is impaired in CCD, leading to a wider and more prominent forehead.
- Widely spaced eyes
Widely spaced eyes, also known as hypertelorism, is another characteristic feature of CCD. It occurs due to the abnormal development of the bones surrounding the eye sockets, resulting in a greater distance between the eyes.
- Small chin
The small chin, or micrognathia, seen in CCD is caused by the underdevelopment of the mandible, the lower jawbone. This underdevelopment results in a receding chin and a distinctive facial profile.
- Short stature
Short stature is a common feature of CCD and is primarily caused by growth hormone deficiency. In addition, skeletal growth problems, such as delayed bone age and small hands and feet, further contribute to the short stature observed in individuals with CCD.
It is important to note that the distinctive appearance associated with CCD can vary among individuals, and not all affected individuals may exhibit all of these features. The severity of the appearance-related manifestations can range from mild to more pronounced, depending on the specific genetic mutation and other factors.
Mobility
In actor cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), the absence or underdevelopment of the clavicles, commonly known as collarbones, has a direct impact on mobility, particularly in the shoulders and arms. This skeletal abnormality affects the range of motion and functionality of the upper limbs.
- Limited Shoulder Movement
The clavicles play a crucial role in stabilizing the shoulder joint and facilitating its movement. In CCD, the absence or hypoplasia of the clavicles impairs the stability of the shoulder, resulting in limited range of motion. Individuals may experience difficulty raising their arms above shoulder height, reaching behind their backs, or performing overhead activities.
- Impaired Arm Function
The clavicles also serve as attachment points for muscles that control arm movements. The absence or underdevelopment of the clavicles affects the proper functioning of these muscles, leading to weakness and reduced coordination in the arms. Individuals with CCD may have difficulty with tasks that require fine motor skills, such as writing, buttoning clothes, or manipulating small objects.
- Posture and Balance
The clavicles contribute to overall posture and balance. In CCD, the absence or hypoplasia of the clavicles can alter the alignment of the shoulders and head, affecting an individual's posture. Additionally, it can impact balance and coordination, making activities like walking, running, or standing for extended periods more challenging.
- Quality of Life
The limited mobility associated with CCD can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life. It can hinder their ability to perform everyday tasks, participate in physical activities, and engage in social interactions. The challenges faced in mobility can affect their independence, self-esteem, and overall well-being.
Understanding the connection between clavicular abnormalities and mobility impairments in CCD is essential for developing appropriate therapeutic interventions. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and assistive devices can help individuals with CCD improve their range of motion, strengthen their muscles, and enhance their functional abilities. Addressing these mobility limitations can significantly improve their quality of life and empower them to live more independently.
Hearing
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of bones and teeth. It is caused by mutations in the RUNX2 gene, which is responsible for regulating the development of bones and teeth. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene can lead to a number of problems, including hearing loss.
- Abnormal bone growth
One of the most common problems associated with CCD is abnormal bone growth. This can lead to a number of problems, including hearing loss. The bones that surround the ear can become thickened and malformed, which can block the sound waves from reaching the inner ear. This can lead to conductive hearing loss, which is a type of hearing loss that occurs when sound waves cannot reach the inner ear.
- Nerve damage
In some cases, CCD can also lead to nerve damage. This can damage the nerves that are responsible for hearing, which can lead to sensorineural hearing loss. Sensorineural hearing loss is a type of hearing loss that occurs when the nerves that are responsible for hearing are damaged.
- Other factors
There are a number of other factors that can contribute to hearing loss in people with CCD. These factors include ear infections, allergies, and exposure to loud noise.
Hearing loss can have a significant impact on a person's life. It can make it difficult to communicate, learn, and socialize. There are a number of different treatments for hearing loss, including hearing aids, cochlear implants, and surgery. The best treatment for hearing loss will vary depending on the individual.
Vision
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of bones and teeth. It is caused by mutations in the RUNX2 gene, which is responsible for regulating the development of bones and teeth. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene can lead to a number of problems, including vision problems.
One of the most common vision problems associated with CCD is strabismus, also known as crossed eyes. Strabismus occurs when the eyes are not properly aligned, which can lead to double vision and other vision problems. Strabismus can be caused by a number of factors, including abnormal bone growth around the eyes. In people with CCD, the bones that surround the eyes can be malformed, which can lead to strabismus.
Another vision problem that can be associated with CCD is nystagmus. Nystagmus is a condition that causes the eyes to move rapidly and involuntarily. Nystagmus can be caused by a number of factors, including nerve damage. In people with CCD, the nerves that are responsible for controlling eye movements can be damaged, which can lead to nystagmus.
Vision problems can have a significant impact on a person's life. They can make it difficult to see clearly, which can interfere with learning, working, and other activities. There are a number of different treatments for vision problems, including glasses, contact lenses, and surgery. The best treatment for vision problems will vary depending on the individual.
Joint pain
Joint pain is a common symptom of actor cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of bones and teeth. CCD is caused by mutations in the RUNX2 gene, which is responsible for regulating the development of bones and teeth. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene can lead to a number of problems, including joint pain.
- Abnormal bone growth
One of the most common problems associated with CCD is abnormal bone growth. This can lead to a number of problems, including joint pain. The bones that surround the joints can become thickened and malformed, which can put pressure on the joints and cause pain. In addition, the abnormal bone growth can lead to instability in the joints, which can also cause pain.
- Arthritis
People with CCD are also at an increased risk of developing arthritis. Arthritis is a condition that causes inflammation of the joints. Inflammation of the joints can lead to pain, swelling, and stiffness. There are a number of different types of arthritis, and the type of arthritis that a person with CCD develops will depend on the individual.
- Other factors
There are a number of other factors that can contribute to joint pain in people with CCD. These factors include obesity, muscle weakness, and nerve damage. Obesity can put extra stress on the joints, which can lead to pain. Muscle weakness can also lead to joint pain, as the muscles are not able to support the joints properly. Nerve damage can also cause joint pain, as the nerves are not able to send signals to the muscles properly.
Joint pain can have a significant impact on a person's life. It can make it difficult to walk, stand, or sit for long periods of time. Joint pain can also make it difficult to perform everyday activities, such as cooking, cleaning, and working. There are a number of different treatments for joint pain, including medication, physical therapy, and surgery. The best treatment for joint pain will vary depending on the individual.
Treatment
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of bones and teeth. It is caused by mutations in the RUNX2 gene, which is responsible for regulating the development of bones and teeth. Mutations in the RUNX2 gene can lead to a number of problems, including:
- Abnormal bone growth
One of the most common problems associated with actor cleidocranial dysplasia is abnormal bone growth. This can lead to a number of problems, including joint pain, limited mobility, and vision problems.
- Dental problems
People with actor cleidocranial dysplasia may have missing or peg-shaped teeth, and their teeth may be more susceptible to cavities and other dental problems.
- Hearing loss
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia can lead to hearing loss in some cases. This is caused by abnormal bone growth around the ear, which can block sound waves from reaching the inner ear.
There is no cure for actor cleidocranial dysplasia, but treatment can help to manage the symptoms of the condition and improve the quality of life for people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia. Treatment may include:
- Surgery
Surgery may be necessary to correct bone deformities, such as a cleft palate or a deviated septum. Surgery can also be used to improve hearing or vision.
- Dental care
People with actor cleidocranial dysplasia require regular dental care to prevent cavities and other dental problems.
- Physical therapy
Physical therapy can help to improve range of motion and strength in people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia.
Treatment for actor cleidocranial dysplasia is individualized and will vary depending on the severity of the condition and the specific symptoms that are present. With proper treatment, people with actor cleidocranial dysplasia can live full and active lives.
Frequently Asked Questions about Actor Cleidocranial Dysplasia
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is a rare condition that can cause a variety of symptoms, including distinctive facial features, dental problems, and skeletal abnormalities. In this FAQ section, we aim to provide answers to some common questions about the condition.
Question 1: What is the primary cause of actor cleidocranial dysplasia?
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is caused by mutations in the RUNX2 gene, which is responsible for regulating the development of bones and teeth.
Question 2: What are the most common symptoms of CCD?
The most common symptoms of CCD include:
- Broad forehead
- Widely spaced eyes
- Small chin
- Short stature
- Dental problems (missing or peg-shaped teeth, increased susceptibility to cavities)
- Skeletal abnormalities (short clavicles, delayed ossification of the skull)
Question 3: How is CCD diagnosed?
CCD is typically diagnosed based on a physical examination and a review of the individual's medical history. Genetic testing can also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Question 4: Is there a cure for CCD?
Currently, there is no cure for CCD. Treatment focuses on managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals with the condition.
Question 5: What are the treatment options for CCD?
Treatment options for CCD may include:
- Surgery to correct bone deformities
- Dental care to address dental problems
- Physical therapy to improve mobility and range of motion
Question 6: What is the prognosis for individuals with CCD?
The prognosis for individuals with CCD varies depending on the severity of the condition. With proper medical care and support, many individuals with CCD can live full and active lives.
In addition to these questions, it is important to recognize that CCD is a complex condition that can affect individuals differently. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
Transitioning to the next article section: This concludes our FAQ section on actor cleidocranial dysplasia. For further information, please refer to the provided resources or seek guidance from medical professionals.
Tips for Managing Actor Cleidocranial Dysplasia
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is a rare condition that can affect the development of bones and teeth. While there is no cure for CCD, there are a number of things that can be done to manage the condition and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Tip 1: Seek Regular Medical Care
Regular medical check-ups are essential for individuals with CCD. These check-ups allow doctors to monitor the condition and provide early intervention for any potential complications.
Tip 2: Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
People with CCD are more susceptible to dental problems, so it is important to maintain good oral hygiene. This includes brushing and flossing regularly, and seeing a dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings.
Tip 3: Participate in Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help to improve range of motion and strength in individuals with CCD. This can help to reduce pain and improve mobility.
Tip 4: Consider Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct bone deformities or improve hearing or vision. Surgery can be a complex procedure, so it is important to discuss the risks and benefits with a doctor before making a decision.
Tip 5: Join a Support Group
Joining a support group can provide individuals with CCD with the opportunity to connect with others who are going through similar experiences. Support groups can offer emotional support and practical advice.
Tip 6: Stay Informed about CCD
Staying informed about CCD can help individuals to better understand their condition and make informed decisions about their care. There are a number of resources available online and from support groups.
Tip 7: Be Patient and Persistent
Managing CCD can be a lifelong journey. It is important to be patient and persistent in seeking treatment and support. With the right care, individuals with CCD can live full and active lives.
Summary
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia is a rare condition that can affect the development of bones and teeth. While there is no cure for CCD, there are a number of things that can be done to manage the condition and improve the quality of life for those affected. By following these tips, individuals with CCD can take an active role in their own care and well-being.
Conclusion
Actor cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD) is a rare genetic condition that affects the development of bones and teeth. It is caused by mutations in the RUNX2 gene, which plays a crucial role in bone formation. CCD can lead to a variety of symptoms, including distinctive facial features, dental problems, skeletal abnormalities, hearing loss, vision problems, and joint pain.
While there is no cure for CCD, treatment can help to manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. Treatment options include surgery, dental care, physical therapy, and support groups. It is important for individuals with CCD to seek regular medical care, maintain good oral hygiene, participate in physical therapy, and stay informed about the condition. With proper care and support, individuals with CCD can live full and active lives.
Unveiling The Enigma: Ellen Barkin's Journey Unveiled
Unveiling The Secrets: Michael Keaton's Son Revealed
Unlocking The Impact Of Sarah Sanders' Height: Insights And Revelations
Stranger Things star Gaten Matarazzo says second surgery for rare bone
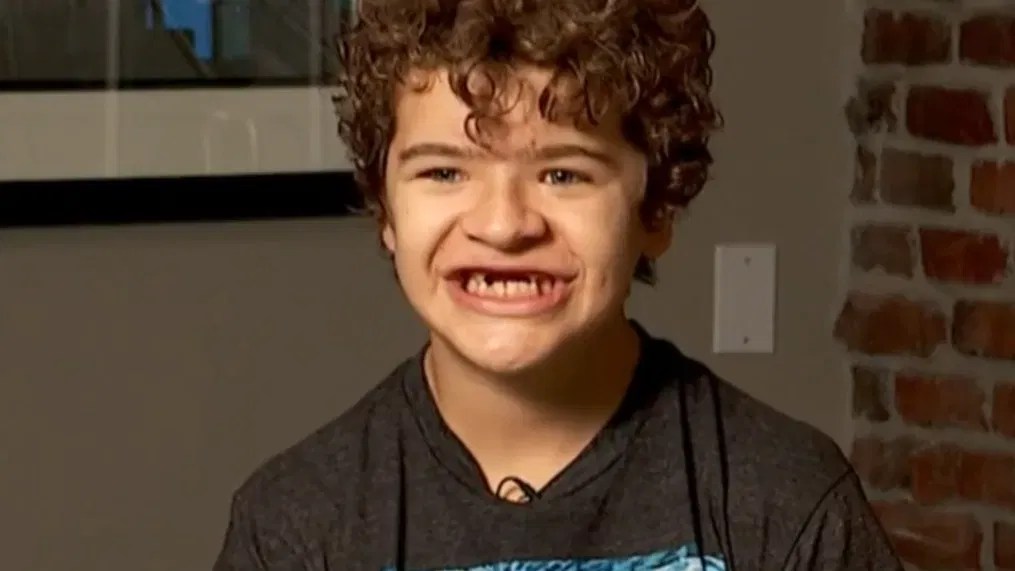

'Stranger Things' actor uses his success to bring awareness to rare disease
ncG1vNJzZmihpKrCb63MrGpnnJmctrWty6ianpmeqL2ir8SsZZynnWSupMDOq2ScpJWesbCv0ZqlopmcYrG6v8%2BlmKyhkWO1tbnL